COLOCANDO B302 NUMA REDE BLE MESH COM Apache Mynewt
(SEGGER JTAG)
O objetivo deste BLOG é demonstrar de forma simplificada como é possível fazer com que o módulo u-BLOX NINA B302 seja um nó de uma REDE MESH (através do Apache Mynewt) e assim poder controlar uma lâmpada a qual é também um nó desta mesma REDE MESH.
Foram utilizados BREAKOUTS u-BLOX NINA B302 para testes. Como provisioning foi utilizado um RASPBERRY PI ZERO W.
MESH
Com o Bluetooth Mesh, não há necessidade de uma rede compartilhada como WiFi. Cada nó da malha pode retransmitir mensagens para outros nós da malha. Para que as nossas lâmpadas pudessem transmitir mensagens de ligar / desligar umas às outras por toda a casa ... Talvez fora de casa também! (Pense em luzes de Natal)
Agora, o Bluetooth Mesh é incrivelmente complicado e difícil de entender ... Então, vou explicar em pequenos pedaços (enquanto estou aprendendo sozinho!)
-Lup Yuen Lee
Sobre Apache Mynewt
Construído para wireless
Atenda às demandas de seu aplicativo a partir de uma variedade de pilhas de rede de código aberto, por exemplo. BLE 5, Bluetooth Mesh, Wi-Fi, LoRaWAN e muito mais ...
Implementação flexível e poderosa do BLE 5 (NimBLE)
- Full stack, host only ou controller only - a sua escolha
- Máximo rendimento de 2Mbps
- Mais de 32 conexões simultâneas, múltiplas conexões em funções centrais e periféricas simultâneas
Mais sobre o NimBLE ...
- Suporte LoRa PHY e LoRaWAN
- Rádio LoRa PHY / transceptor (SX1276)
- Protocolo LoRaWAN para terminais de classe A e classe C
- API para uso de aplicativos com um aplicativo de amostra
Bluetooth Mesh
- Modelos de Fundação (função de servidor)
- Portadores de aprovisionamento: PB-ADV e PB-GATT
- Portadores de publicidade e GATT para transporte de mensagens
- Recursos opcionais de retransmissão e proxy
Suporte nativo para TCP / IP, UDP
- Suporta protocolos para redes restritas, por ex. CoAP e 6LoWPAN
Segurança desde o início
Certifique-se de que a segurança esteja incorporada no código, bem como o gerenciamento do ciclo de vida do produto.
- Bootloader seguro para verificar a integridade e autenticidade do firmware
- Identidade do dispositivo para provisionamento seguro
- Transferências de dados autenticadas, autorizadas e criptografadas
- Interface abstraída para aproveitar a segurança de hardware
- Mais sobre a segurança do Mynewt OS ..
Operações prontas
Prepare sua rede de bilhões de IoT para monitoramento, solução de problemas, gerenciamento e atualização remotos.
- Módulo de gerenciamento de imagens para permitir atualizações de firmware remotas eficientes, com reconhecimento de falhas e confiáveis
- Módulos de log que podem ser chamados em vários níveis de granularidade, incluindo logs de reinicialização especializados
- Módulos de estatísticas ricamente instrumentados para componentes do SO e interfaces de rede
- Fácil de usar a estrutura do sensor para conectar uma variedade de sensores
- Descoberta automática e gerenciamento usando OIC1.1, o padrão de plataforma IoT da OCF (Open Connectivity Foundation)
Fácil de usar
Componha, ajuste e crie sua imagem em horas ou até minutos.
- Inicialização de hardware em arquivo de configuração única para o BSP escolhido
- Inicialização de parâmetros de serviço em um único arquivo de configuração para o módulo escolhido, e. Controlador BLE
- Gerenciamento inteligente de pacotes e construção usando a ferramenta Newt
- Auditorias automáticas de configuração usando o Newt Tool
Espero que você já tenha instalado o mynewt em seu computador, caso contrário leia os outros BLOGS do autor, enfim:
Tenha Segger J-Link instalado
-O EVK-NINA-B3 já possui Software SEGGER J-LINK
Presume-se que você já instalou a ferramenta newt.
Presume-se que você compreenda o básico do sistema operacional mynewt
ROTEIRO
1) Instalando o MyNewt
Instalação
Antes instale o MYNEWT para WINDOWS por qui
Instale MSYS2/MinGW.
Instale com pacman o vim, nano, tar, tree, GIT (no msys32)
Instale o GO
pacman -S mingw-w64-x86_64-go
Instale a versão mais recente (1.6.0) do newt do binário (na pasta bin do GO)
Apache Download Mirrors, jogue em /msys64/home/usuario o apache-mynewt-newt-bin-windows-1.8.0.tgz e execute
tar -xzf apache-mynewt-newt-bin-windows-1.8.0.tgz -C /usr/bin --strip-components=1 apache-mynewt-newt-bin-windows-1.8.0/newt.exe
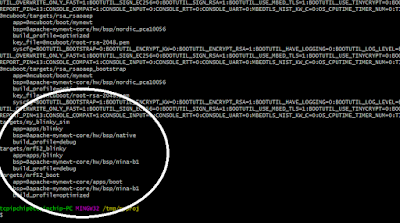
Crie um projeto$ mkdir ~/dev $ cd ~/dev $ newt new myproj Downloading project skeleton from apache/mynewt-blinky... Installing skeleton in myproj... Project myproj successfully created. $ cd myproj $ newt upgrade apache-mynewt-core
Crie os destinos Boot e APP
$ newt target create nrf52_boot $ newt target set nrf52_boot app=@apache-mynewt-core/apps/boot $ newt target set nrf52_boot bsp=@apache-mynewt-core/hw/bsp/nordic_pca10056 $ newt target set nrf52_boot build_profile=optimized
$ newt target create nrf52_blinky $ newt target set nrf52_blinky app=apps/blinky $ newt target set nrf52_blinky bsp=@apache-mynewt-core/hw/bsp/nordic_pca10056 $ newt target set nrf52_blinky build_profile=debug
Veja se criou
$ newt target show targets/nrf52_blinky app=apps/blinky bsp=@apache-mynewt-core/hw/bsp/nordic_pca10056 build_profile=debug targets/nrf52_boot app=@apache-mynewt-core/apps/boot bsp=@apache-mynewt-core/hw/bsp/nordic_pca10056 build_profile=optimized
Gere os executáveis (Boot e APP)
$ newt target set nrf52_boot app=@mcuboot/boot/mynewt $ newt build nrf52_boot Building target targets/nrf52_boot Compiling repos/apache-mynewt-core/boot/bootutil/src/image_ec256.c Compiling repos/apache-mynewt-core/boot/bootutil/src/image_ec.c Compiling repos/apache-mynewt-core/boot/bootutil/src/image_rsa.c Compiling repos/apache-mynewt-core/crypto/mbedtls/src/aes.c Compiling repos/apache-mynewt-core/boot/bootutil/src/loader.c Compiling repos/apache-mynewt-core/boot/bootutil/src/image_validate.c Compiling repos/apache-mynewt-core/boot/bootutil/src/bootutil_misc.c Compiling repos/apache-mynewt-core/apps/boot/src/boot.c ... Archiving sys_mfg.a Archiving sys_sysinit.a Archiving util_mem.a Linking ~/dev/myproj/bin/targets/nrf52_boot/app/apps/boot/boot.elf Target successfully built: targets/nrf52_boot
$ newt build nrf52_blinky Building target targets/nrf52_blinky Assembling repos/apache-mynewt-core/hw/bsp/nrf52dk/src/arch/cortex_m4/gcc_startup_nrf52_split.s Compiling repos/apache-mynewt-core/hw/bsp/nrf52dk/src/sbrk.c Compiling repos/apache-mynewt-core/hw/cmsis-core/src/cmsis_nvic.c Compiling repos/apache-mynewt-core/hw/drivers/uart/uart_hal/src/uart_hal.c Assembling repos/apache-mynewt-core/hw/bsp/nrf52dk/src/arch/cortex_m4/gcc_startup_nrf52.s Compiling apps/blinky/src/main.c ... Archiving sys_mfg.a Archiving sys_sysinit.a Archiving util_mem.a Linking ~/dev/myproj/bin/targets/nrf52_blinky/app/apps/blinky/blinky.elf Target successfully built: targets/nrf52_blinky
Crie a imagem da aplicação
$ newt create-image nrf52_blinky 1.0.0 App image succesfully generated: ~/dev/myproj/bin/targets/nrf52_blinky/app/apps/blinky/blinky.img
2) Instalando APP MESH (mingw32)
newt new mymesh
cd mymesh
newt upgrade -v
newt target create nrf52_boot
newt target set nrf52_boot bsp=@apache-mynewt-core/hw/bsp/nordic_pca10056
newt target set nrf52_boot build_profile=optimized
newt target create nrf52_mesh
newt target set nrf52_mesh app=apps/mymesh
newt target set nrf52_mesh bsp=@apache-mynewt-core/hw/bsp/nordic_pca10056
newt target set nrf52_mesh app=@apache-mynewt-nimble/apps/blemesh_models_example_2
newt target set nrf52_mesh build_profile=optimized
**newt target set nrf52_mesh build_profile=debug
overload .Text in 5k
newt target set nrf52_boot app=@mcuboot/boot/mynewtnewt build nrf52_boot
Alterar em bsp.h os GPIOS para LED_ e BUTTON_ para serem compatíveis com as GPIOS do U-BLOX NINA B302
MSYS ~/dev/myproj/mymesh/repos/apache-mynewt-core/hw/bsp/nordic_pca10056/include/bsp
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
* software distributed under the License is distributed on an
* "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
* KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
* specific language governing permissions and limitations
* under the License.
*/
#ifndef H_BSP_H
#define H_BSP_H
#include <inttypes.h>
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/* Define special stackos sections */
#define sec_data_core __attribute__((section(".data.core")))
#define sec_bss_core __attribute__((section(".bss.core")))
#define sec_bss_nz_core __attribute__((section(".bss.core.nz")))
/* More convenient section placement macros. */
#define bssnz_t sec_bss_nz_core
extern uint8_t _ram_start;
#define RAM_SIZE 0x40000
/* LED pins */
#define LED_1 (13)
#define LED_2 (14)
#define LED_3 (15)
#define LED_4 (16)
#define LED_BLINK_PIN (LED_1)
/* Buttons */
#define BUTTON_1 (11)
#define BUTTON_2 (12)
#define BUTTON_3 (25)
#define BUTTON_4 (27)
/* Arduino pins */
#define ARDUINO_PIN_D0 29
#define ARDUINO_PIN_D1 45
#define ARDUINO_PIN_D2 44
#define ARDUINO_PIN_D3 31
#define ARDUINO_PIN_D4 13
#define ARDUINO_PIN_D5 11
#define ARDUINO_PIN_D6 9
#define ARDUINO_PIN_D7 10
#define ARDUINO_PIN_D8 41
#define ARDUINO_PIN_D9 12
#define ARDUINO_PIN_D10 14
#define ARDUINO_PIN_D11 15
#define ARDUINO_PIN_D12 32
#define ARDUINO_PIN_D13 07
#define ARDUINO_PIN_A0 4
#define ARDUINO_PIN_A1 30
#define ARDUINO_PIN_A2 5
#define ARDUINO_PIN_A3 2
#define ARDUINO_PIN_A4 28
#define ARDUINO_PIN_A5 3
#define ARDUINO_PIN_RX ARDUINO_PIN_D0
#define ARDUINO_PIN_TX ARDUINO_PIN_D1
#define ARDUINO_PIN_SCL 24
#define ARDUINO_PIN_SDA 16
#define ARDUINO_PIN_SCK ARDUINO_PIN_D13
#define ARDUINO_PIN_MOSI ARDUINO_PIN_D11
#define ARDUINO_PIN_MISO ARDUINO_PIN_D12
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* H_BSP_H */
newt build nrf52_mesh
newt create-image nrf52_mesh 0.0.0
$ pacman -S mingw-w64-x86_64-arm-none-eabi-gdb
mudar para sufixo cmd em bsp.yml, caso utilize o WINDOWS
C:\msys32\home\user\dev\mymesh\repos\apache-mynewt-core\hw\bsp\nordic_pca10056
ou no MSYS
/home/Usuario/mymesh/repos/apache-mynewt-core/hw/bsp/nordic_pca10056
bsp.downloadscript: "hw/bsp/nordic_pca10056/nordic_pca10056_download.cmd"
bsp.debugscript: "hw/bsp/nordic_pca10056/nordic_pca10056_debug.cmd"
newt load nrf52_boot
newt load nrf52_mesh
2) Seguir passo a passo o excelente BLOG abaixo
Sobre o BLOG, aqui vão algumas dicas:
- Utilizei SEGGER J-LINK em vez do ST-LINK;
- Tenha em mãos conversores USB-SERIAL para vermos os LOGS da REDE MESH;
- Nodo é visto como SWITCH+LIGHT;
- Foram utilizados 2 NINA B302, compatíveis com do autor do BLOG, ou seja com core NRF52840. NINA B302 como função de SWITCH e NINA B302 como função de LÂMPADA;
- Como Provisioning (
meshctl) da REDE MESH foi utilizado o RASPBERRY PI ZERO W, a compilação do KERNEL no Hardware nativo foi necessária por causa da criptografia AEAD-AES_CCM, que funciona como um serviço seguro no kernel e levou 25 Horas, então sugiro CROSS-COMPILE.Se você vir esta mensagem "Falha ao analisar o arquivo de banco de dados de provisionamento prov_db.json", isso significa que seu kernel ainda não tem a criptografia AEAD-AES_CCM instalada.Para compilação algumas LIBS tiveram que ser acrescentadas e outras passarem por um DOWNGRADE, mas tudo reportado pelo compilador, requer experiência do usuário com Linux.
- Em syscfg.yml se encontra o UUID
BLE_MESH_DEV_UUID: "((uint8_t[16]){0xdd, 0xdd, 0})",
na pasta blemesh_models_example_2
- No blog a versão do BLUEZ é bluez-5.50, mas já está na bluez-5.54;
- Sempre saia do meshctl antes de desligar qualquer nó da malha. Caso contrário, o meshctl pode travar ao tentar sair. (E você precisaria reiniciar seu Raspberry Pi para liberar o driver Bluetooth bloqueado);
- Para se conectar à rede mesh no futuro, basta iniciar meshctl e inserir Connect;
- Eu recomendo fortemente que você faça backup de sua cópia do prov_db.json localizada no diretório inicial pi do seu Raspberry Pi ... Porque o cartão microSD pode ser corrompido facilmente;
- O autor do BLOG utilizou o Microsoft Visual Code, em meus testes utilizei linhas de comando;
- Foi utilizada REDE MESH "Generic e Level" MODE;
- Tenha sempre o Segger J-LINK aberto para apagar as configurações do NÓ MESH, lembre-se de gravar com o APP o BOOT também; Se precisarmos provisionar novamente este nó, teremos que apagar a Flash;
$ JLinkExe -device nRF52 -speed 4000 -if SWD SEGGER J-Link Commander V5.12c (Compiled Apr 21 2016 16:05:51) DLL version V5.12c, compiled Apr 21 2016 16:05:45 Connecting to J-Link via USB...O.K. Firmware: J-Link OB-SAM3U128-V2-NordicSemi compiled Mar 15 2016 18:03:17 Hardware version: V1.00 S/N: 682863966 VTref = 3.300V Type "connect" to establish a target connection, '?' for help J-Link>erase Cortex-M4 identified. Erasing device (0;?i?)... Comparing flash [100%] Done. Erasing flash [100%] Done. Verifying flash [100%] Done. J-Link: Flash download: Total time needed: 0.363s (Prepare: 0.093s, Compare: 0.000s, Erase: 0.262s, Program: 0.000s, Verify: 0.000s, Restore: 0.008s) Erasing done. J-Link>exit $
- Raspberry e Nó devem estar bem próximos;
- Crie um BACKUP do config do meshctl
3) Testes efetuados com dois Nós (imagens)
Gravando BOOT e APP no NINA B302
Por ser Tratar de BLE, SCANNER já encontrou o Nó
Meshctl encontrou Nó NINA B302 também.
NINA B302 fazendo Advertising para ser "Provisionado"
Mesh Provisioning
Provisioned (SWITCH)
Guarda endereço no tabela prov_db.json
APP KEY
Provisioned (LIGHT)
Enfim, siga o roteiro do Autor do BLOG (REF) para primeiro Nó
meshctl Command | Description |
|---|---|
cd ~ | Mesh detail file prov_db.json will be located in Raspberry Pi home directory |
cp bluez-5.50/mesh/local_node.json . ; cp bluez-5.50/mesh/prov_db.json . | Only for first node. Provision the mesh with an empty prov_db.json |
meshctl | Launch meshctl |
Press Enter | To reveal meshctl prompt |
discover-unprovisioned on | Discover unprovisioned devices. We should see Device UUID: dddd0000000000000000000000000000 |
provision dddd0000000000000000000000000000 | Begin provisioning our device. In Visual Studio Code Console Log, look for the message OOB String: <key> |
At Enter key prompt, enter the OOB String key | We should see Provision success. Assigned Primary Unicast 0100. The new node has been assigned Unicast Address 0100. From now on we shall use this Unicast Address for any target command. |
menu config | Enter Configuration Menu |
target 0100 | Target the new node |
appkey-add 1 | Load AppKey #1 from prov_db.json |
bind 0 1 1000 | Expose Generic On/Off Server, locked by AppKey #1 |
bind 0 1 1001 | Expose Generic On/Off Client, locked by AppKey #1 |
bind 0 1 1002 | Expose Generic Level Server, locked by AppKey #1 |
bind 0 1 1003 | Expose Generic Level Client, locked by AppKey #1 |
sub-add 0100 c000 1000 | Subscribe to On/Off Updates at Group Address c000 |
sub-add 0100 c000 1002 | Subscribe to Level Updates at Group Address c000 |
pub-set 0100 c000 1 0 5 1001 | Publish On/Off Updates at Group Address c000 |
pub-set 0100 c000 1 0 5 1003 | Publish Level Updates at Group Address c000 |
back | Return to top level menu |
menu onoff | Enter On/Off Menu for testing the new node |
target 0100 | Target the new node |
onoff 0 | Set On/Off Client to 0. LED on nRF52 board should turn off. |
get | Show On/Off Client Status. Should show 0 |
onoff 1 | Set On/Off Client to 1. LED on nRF52 board should turn on. |
get | Show On/Off Client Status. Should show 1 |
exit | Exit meshctl. Mesh details have been updated into prov_db.json |
Siga o roteiro do Autor do BLOG (REF) para o segundo nó
meshctl Command | Description |
|---|---|
cd ~ | meshctl will use mesh detail file prov_db.json located in Raspberry Pi home directory |
meshctl | Launch meshctl |
Press Enter | To reveal meshctl prompt |
discover-unprovisioned on | Discover unprovisioned devices. We should see Device UUID: dddd0000000000000000000000000000 |
provision dddd0000000000000000000000000000 | Begin provisioning our device. In Visual Studio Code Console Log, look for the message OOB String: <key> |
At Enter key prompt, enter the OOB String key | We should see Provision success. Assigned Primary Unicast 0102. The new node has been assigned Unicast Address 0102. From now on we shall use this Unicast Address for any target command. |
menu config | Enter Configuration Menu |
target 0102 | Target the new node |
appkey-add 1 | Load AppKey #1 from prov_db.json |
bind 0 1 1000 | Expose Generic On/Off Server, locked by AppKey #1 |
bind 0 1 1001 | Expose Generic On/Off Client, locked by AppKey #1 |
bind 0 1 1002 | Expose Generic Level Server, locked by AppKey #1 |
bind 0 1 1003 | Expose Generic Level Client, locked by AppKey #1 |
sub-add 0102 c000 1000 | Subscribe to On/Off Updates at Group Address c000 |
sub-add 0102 c000 1002 | Subscribe to Level Updates at Group Address c000 |
pub-set 0102 c000 1 0 5 1001 | Publish On/Off Updates at Group Address c000 |
pub-set 0102 c000 1 0 5 1003 | Publish Level Updates at Group Address c000 |
back | Return to top level menu |
menu onoff | Enter On/Off Menu for testing the new node |
target 0102 | Target the new node |
onoff 0 | Set On/Off Client to Off. LED on nRF52 board should turn off. |
get | Show On/Off Client Status. Should show 0 |
onoff 1 | Set On/Off Client to On. LED on nRF52 board should turn on. |
get | Show On/Off Client Status. Should show 1 |
exit | Exit meshctl. Mesh details have been updated into prov_db.json |
Testes com dois Nós
Download
Raspberry Pi Zero W provisioning
Suporte: suporte@smartcore.com.br
Referências:
Thanks to Yup Luen Lee
Sobre a SMARTCORE
A SmartCore fornece módulos para comunicação wireless, biometria, conectividade, rastreamento e automação.
Nosso portifólio inclui modem 2G/3G/4G/NB-IoT/Cat.M, satelital, módulos WiFi, Bluetooth, GNSS / GPS, Sigfox, LoRa, leitor de cartão, leitor QR code, mecanismo de impressão, mini-board PC, antena, pigtail, LCD, bateria, repetidor GPS e sensores.
Mais detalhes em www.smartcore.com.br